Protsessor – CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Arvuti “südameks” on keskseade e. protsessor (CPU – Central Processing Unit). Protsessor sooritab enamuse arvuti tööks vajalikest arvutustest, seetõttu sõltub arvuti kiirus kõige rohkem protsessori kiirusest ehk taktsagedusest, mida mõõdetakse hertsides, mega/giga hertsides. Taktsagedus määrab palju loogikatehteid suudab antud protsessor ühes sekundis teha.
Protsessor paikneb oma pesas.
Tuntumad protsessori tootjad on Intel ja AMD.
Protsessori valimise juures vaadatakse peamiselt 2 näitaja:
Esiteks millisest Protsessori seeriast on protsessor (Näiteks: Intel Core I3, I5, I7, I9.) ja kui suur on protsessori taktsagedus megahertsides (Ghz). See parameeterist sõltub, kui palju loogikatehteid suudab antub protsessot ühes sekundis teha.
Protsessori seeria mõjutab arvuti kiirust päris oluliselt, sest erinevates protsessori tüüpides on kasutatud erinevaid tehnoloogiad, mis lubavad erinevaid võimalusi.
Protsessori kiirus sõltub operatiivmälust, mida vähem on operatiivmälu seda aeglasemalt protsessor töötab ja seda aeglasem on ka arvuti.
Protsessorile on ka vajalik radiaator ja ventilaator. Igale protsessori margile on tehtud ka erinevad radiaatorid (uuena ostes on need kompletselt koos). Kui protsessor juba olemas tuleb talle poest ka vastav radiaator (cooler) küsida.
Tehnilised andmed
Kõige olulisem protsessori omadus on tema töökiirus ehk see, kui palju instruktsioone ta suudab ühe ajaühiku jooksul täita. Kaks olulist komponenti, mis määravad töökiiruse on:
- protsessori taktsagedus mõõdetakse Hertsides (MHz ja GHz)
- protsessori arhitektuur
- protsessori läbilaskevõime (mõõdetakse bittides)
On olemas ka mitme tuumalisi protsessoreid alates 1 tuumalisest kuni 24 tuumaliseni välja. Plaanitakse teha ka 80 tuumalist protsessorit.

How to Find the Generation of Intel® Core™ Processors
To identify your Intel Core generation, you need first to identify the processor. Refer to how to identify your Intel® Processor and note the number.
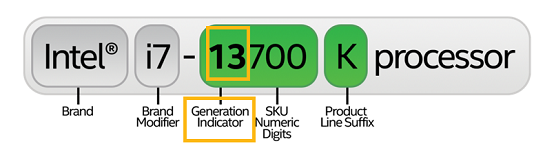
In Intel® Core™ Processors, the generation of the processor is the number (or the two numbers) after the i9, i7, i5, or i3, as shown in the example below.
Note: This method applies only on Intel® Core™ Processors and does not apply on Intel® Pentium®, Intel® Celeron®, or Intel® Xeon®.
Here is an example with 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor.
Here are some examples by processor generation:
14th Gen example
- Intel® Core™ Processor i9-14900K is 14th Gen because number 14 is listed after i9.
13th Gen example
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-13700K is 13th Gen because number 13 is listed after i7.
12th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-12700K is 12th Gen because number 12 is listed after i7.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i9-12900HX is 12th Gen because number 12 is listed after i9.
11th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-1165G7 is 11th Gen because number 11 is listed after i7.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-1130G7 is 11th Gen because number 11 is listed after i5.
10th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-1065G7 is 10th Gen because number 10 is listed after i7.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-10210U is 10th Gen because number 10 is listed after i5.
9th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i9-9900K is 9th Gen because number 9 is listed after i9.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-9300H is 9th Gen number 9 is listed after i5.
8th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-8650U is 8th Gen because number 8 is listed after i7.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-8600 is 8th Gen because number 8 is listed after i5.
7th Gen examples
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-7200U is 7th Gen because number 7 is listed after i5.
- Intel® Core™ Processor i3-7350K is 7th Gen because number 7 is listed after i3.
6th Gen example
- Intel® Core™ Processor i5-6400T is 6th Gen because number 6 is listed after i5.
5th Gen example
- Intel® Core™ Processor i7-5650U is 5th Gen because number 5 is listed after i7.
4th Gen example
- Intel® Core™ Processor i3-4350T is 4th Gen because number 4 is listed after i3.